Windows 11 comes with built-in management console and Control Panel files that can be used for quick access to manage your OS settings. This is especially useful for both sysadmins and netadmins since they regularly need to access the system settings to troubleshoot and configure them.
Since we at iTechtics also use these management interfaces regularly, this post discusses 10 of our most-used and handy Microsoft Management Consoles (MMC) and what they can be used for. Moreover, all of these are also pre-installed in Windows 10 as well, having the same interface and functions.
Table of Contents
There are a total of 22 management consoles and 18 Control Panel files in Windows. Each of these performs a different function while some consoles include a combination of the other ones. This can be accessed quickly by inputting the associated command in Run or the Command Prompt
We shall only be discussing the management consoles in this post. Here are the Microsoft Management Consoles that we think you should definitely know about.
Most Used Management Consoles in Windows 11
Computer Management Console
Command: compmgmt.msc
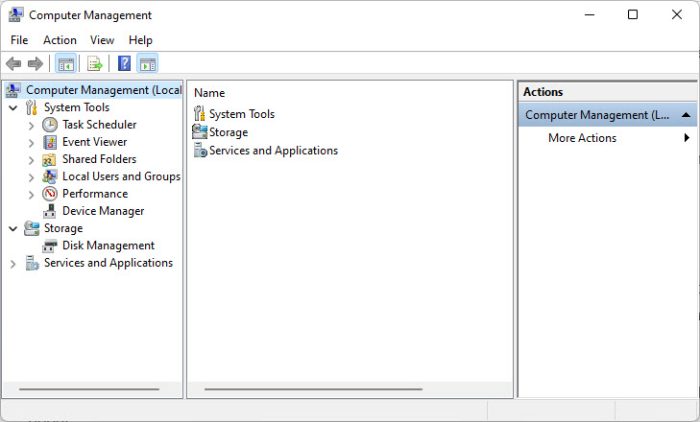
The Computer Management console includes the following consoles:
- Task Scheduler
- Event Viewer
- Shared Folders
- Local Users and Groups
- Performance Monitor
- Device Manager
- Disk Management
- Services
- WMI Control
The Computer Management console holds an accumulation of different consoles, and each of these consoles can also be accessed separately, as you will learn in the sections below.
Local Security Policy Console
Command: secpol.msc
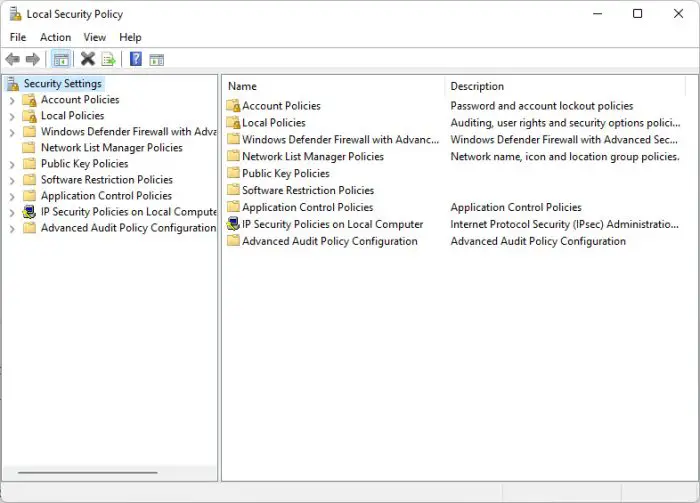
The Local Security Policy console can be used to manage your system’s security policies. User Account Control (UAC) is also managed through this console, amongst many other security settings.
Local Group Policy Console
Command: gpedit.msc
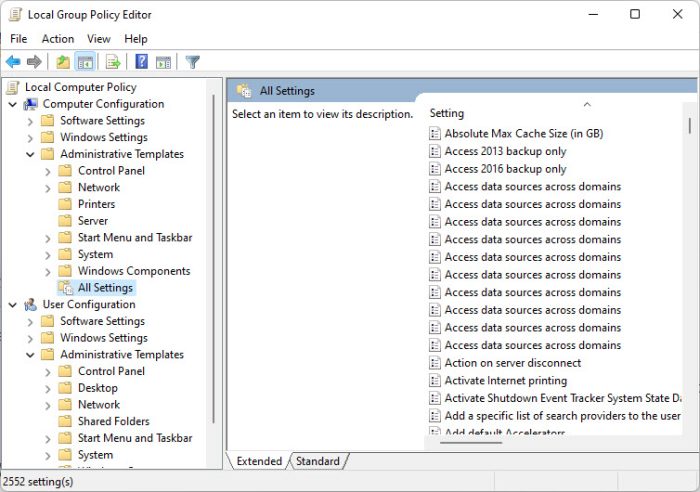
The Group Policy Editor is used to control how your system behaves. Sysadmins within an organization can control these policies via Windows Server to limit a user’s experience and enhance the overall security when connected to a Domain Controller.
Disk Management Console
Command: diskmgmt.msc
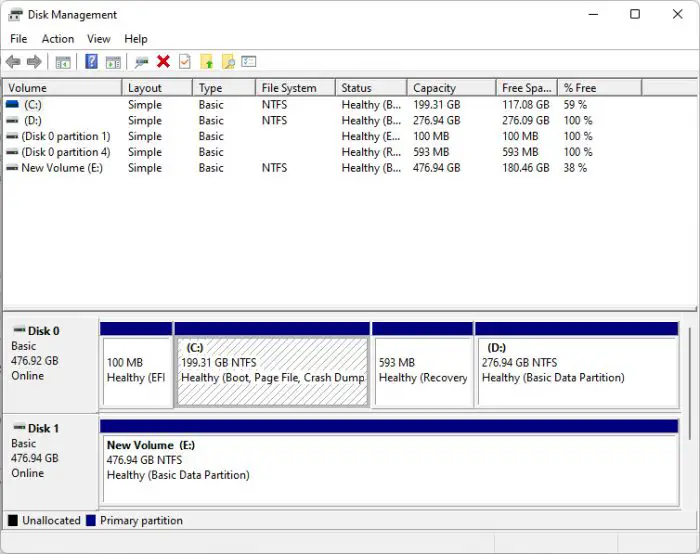
The Disk Management console provides several options to manage your storage partitions and volumes, such as formatting or creating new partitions, shrinking or expanding them, or assigning/changing drive letters.
Event Viewer Console
Command: eventvwr.msc
This console is ideal for troubleshooting your operating system. It records all events occurring on your machine, including the details for any errors and BSODs.
Local Users and Groups Console
Command: lusrmgr.msc
The Local Users and Groups console can be used to create, delete and manage user accounts on your device. You can also add or remove them from various groups that define their rights and privileges or simply change their passwords.
Service Console
Command: services.msc
This console shows all the services needed to run the operating system. We often use it to start, stop, or restart a service if and when required. If you want to stop a service from running automatically, the Services console is where you come from.
Hyper-V Management Console
Command: virtmgmt.msc
This management console lets the user manage their Virtual Machines (VMs) on top of the virtualization technology. Furthermore, this console allows you to connect to the VMs, manage their specifications, start and stop them, manage the virtual network interfaces, etc.
Shared Folders Console
Command: fsmgmt.msc
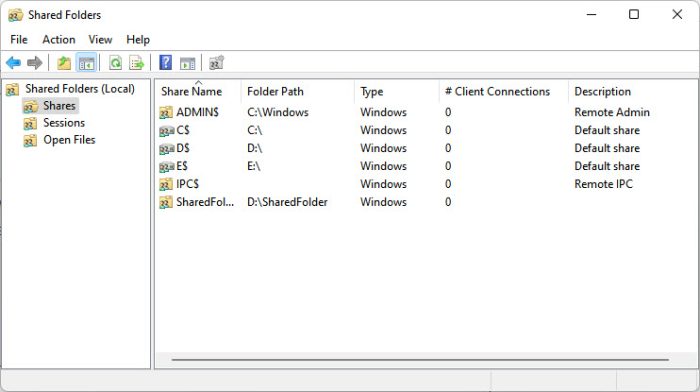
Through this console, you can manage your shared folders and their permissions. You can allow or disallow devices or user accounts on your network to access your shared content, or simply manage its security and rights for each individual person/computer.
Performance Monitoring Console
Command: perfmon.msc
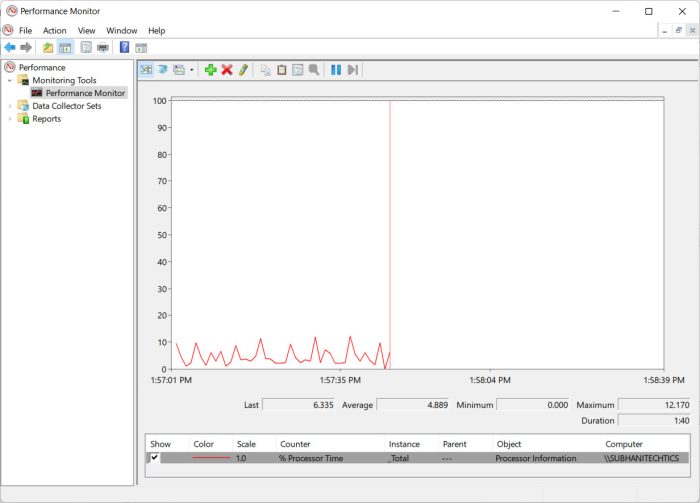
The Monitoring console allows you to keep a check on your system’s resources. This includes the processor, network traffic, print queue, memory, disk, battery, and much more. Each item can be monitored through this tool using a graphical representation of the statistics.
How to Check Commands for all Windows Management Consoles
If you have forgotten the command for a specific console, or just want to see which management consoles are available on your computer, run the following command in Windows PowerShell:
Get-ChildItem -Path C:\Windows\system32\* -Include *.msc | Sort-Object -Property Extension | Select-Object -Property Name | Format-Wide -Column 1
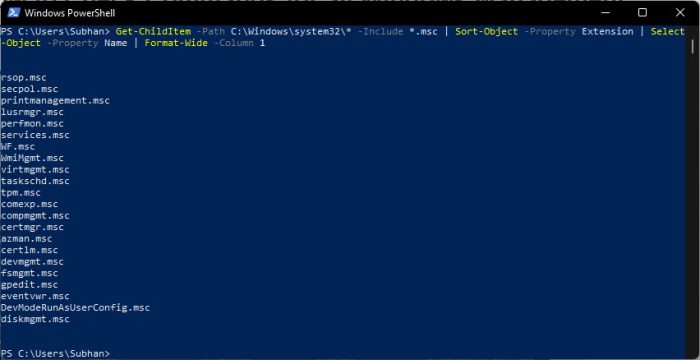
As you can see in the image above, all of the management consoles are visible with their cmdlets that you can enter in Run to access.
Create Your Own Customized Management Console
Most Microsoft Management Consoles only cater to single elements within the OS, except for the Computer Management console. However, you can create your own MMC which includes all of the consoles that you mostly use, all in one place. This will save you the hassle of opening up each management console individually.
Here is how you can create a customized management console:
- Open the root Microsoft Management Console by typing in mmc in Run.
- Now click File from the top menu and then click Add/Remove snap-in.

- Now select the console you want to add to your customized mmc from the list under “Available Snap-ins” and then click Add.

- If prompted for more options, select the one that fits your requirements and click Ok/Finish.

- Now repeat steps 3 and 4 until you have added all the consoles that you want to.
- When added, click OK.

- Now click on File again and then click Save. Now browse to the location where you want to save your customized console, set a name, and click Save.

Your customized management console has now been saved. You can now run it directly without having to open up various consoles each time you want to change your device configuration.
FAQs
How do I bring up the Microsoft Management Console?
You can launch an MMC by searching for it through the Start Menu, or open the root MMC by typing in mmc in Run. From there, click File and then Add/Remove Snap-in. Choose the console you want to run and click Add. Close the window by clicking OK. You now have the management console that you want to run.
How do I get to the root console?
Open the root console by typing in mmc in Run. From there, click File and then Add/Remove Snap-in to open any of the consoles available on your system.
What is MMC.exe process?
mmc.exe is the process behind running the Microsoft Management Console in a Windows environment.





